A common example of a coupled reaction is the formation of ATP a nucleotide that contains chemical energy that is broken down for metabolic uses. For example the anaerobic oxidation of methane in the presence of seawater sulfates is an important microbial reaction in the gas hydrate zones of Earths seafloors.
When a compound loses an electron or is oxidized another compound gains the electron or is reduced.
. Else_NT-DEMIREL_CH011qxd 1192008 1114 AM Page 542. Endergonic reactions require energy so that they can form polymers from monomers. How do enzymes catalyze chemical reactions.
We can use this relationship to describe coupled red-ox reactions in biological systems. The reversible work for an electrochemical cell such as a battery is w nFɛ where n is the number of moles of electrons involved in the reaction F is Faradays constant and ε. Thermodynamics and biological systems.
3 points A coupled reaction is where endergonic reactions are coupled with exergonic reactions. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Cells commonly employ either of two mechanisms to cause endergonic reactions to take place.
Explain two advantages of the presence of coupled reactions in nearly all biological systems. These microscopic events may be for instance sets of coupled reactions that lead to some observable change of state a different phenotype in the parlance of biology. These redox reactions take place in enzyme complexes situated within the mitochondrial membrane.
They rely on the transfer of inorganic phosphates to provide energy. Electron transfer ET through and between proteins is a fundamental biological process. Check all that describe coupled reactions Check All That Apply One part of the reaction requires ATP.
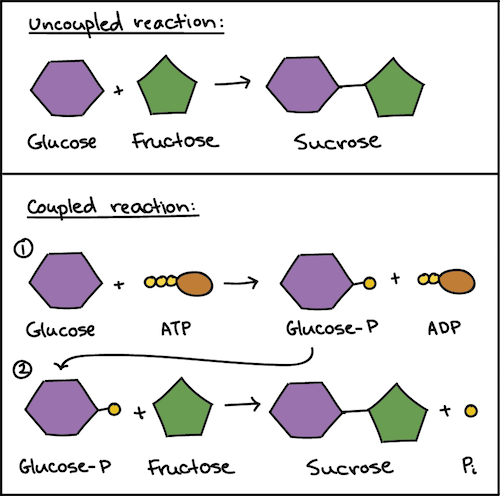
One part of the reaction makes ATP. Use the equation above and the equation G Gº RT In In. An example of a coupled reaction is the conversion of ADP Pi ATP which is linked to an oxidation reaction during glycolysis.
Both parts of the reaction are exergonic They are found in biological systems. If the system is able to exchange heat with the. Describe the connection between these reactions in terms of energy production.
System subcompartments are usually coupled in the models using material transfer reactions or as rules that alter the kinetic parameters. Describe the process of binary fission. Inorganic reactions and biological reactions on Earth often link sulfur to carbon and in so doing govern the molecular distributions of the two elements King and McLennan 2010.
Electron transport chain complexes. A coupled reaction consists of two linked reactions occurring at the same time. In what ways do biological systems make use of regulating rates of reactions.
For a chemical reaction in a test-tube all the work potential change in free-energy or the -DG of the process is squandered as heat. A product of a reaction in a metabolic pathway is generally the reactant for the subsequent step in the pathway. What does it mean when we say that two reactions are coupled.
As pointed out by Atkinson 1977 the coupled reaction is a different reaction to the reaction we are trying to drive with different overall stoichiometry and hence a different overall equilibrium constant Atkinson 1977 p52. Cellular respiration in eukaryotes involves a series of coordinated enzyme-catalyzed reactions that capture energy from biological macromolecules. 40 Energy - requiring reactions can occur in biological systems because they can be coupled with reactions that are A exergonic.
C spontaneous and endergonic. This difference in proton concentration between the mitochondrial matrix and. Coupled Reaction in Bioenergetics.
The analysis of protein ET reactions is complicated by the fact that non-ET processes might. A common group transfer reaction in biological systems is one that is used to produce α-amino acids that can then be used for protein synthesis. Which methods in the lab can be used to measure growth.
Introduction Living Organisms and Chemical reactions Biological processes are the processes vital for a living organism to live. In this reaction one α-amino acid serves as the donor molecule and an α-keto acid these molecules contain a carboxylic acid functional group and a ketone functional group separated by one α-carbon serves as the acceptor. 1st Semester Department of Life Science and Bioinformatics Assam University Silchar 2.
When the energy released by an exergonic reaction is used to drive an endergonic reaction YZ--YZ endergonic - requires energy AX-- AX endergonic. These microscopic events involve enzyme complexes and coupled reaction pathways in cells which are not just scaled down versions of beaker-sized laboratory systems. Biological oxidation is an energy-producing reaction in living cells and it is coupled with a reduction reaction.
These relations show the equality between the w ork of the excess pressure and the increase in surface. What Is a Coupled Reaction in Biology. Coupling between reactions A change of state of a system which occurs independently of coupling to the surroundings cannot conserve the work potential associated with the change.
ENE-1H3 Energy-related pathways in biological systems are sequential to allow for more controlled and efficient transfer of energy. These redox reactions transfer electrons down the electron transport chain which is coupled to the proton motive force. No enzyme for example can push any reaction past its position of.
For example material can be transported in and out of organelles or nucleus to exchange material with the cytoplasm. One mechanism illustrated above by the glycolysis example is to create reactant and product concentrations that are. Coupled with cellular processes that require energy.
Basic biological reactions 1. The electron transport chain transfers energy from electrons in a series of coupled reactions that establish an electrochemical gradient across membranes-. A coupled reaction does not push a reaction past its equilibrium see Atkinson 1977 p52.
Oxidation-reduction redox reactions represent the main source of biological energy. Exergonic reactions release energy when they break down polymers into monomers. Basic Biological Reactions Presented by.
ATP stores energy in the. A coupled reaction is a reaction with a common intermediate that results in energy being transferred from one side of the reaction to the other. Loss of order or energy flow results in death.
The rates of ET depend upon the thermodynamic driving force the reorganization energy and the degree of electronic coupling between the reactant and product states.

What Is The Purpose Of Coupled Reactions

Common Functional Groups In Biochemistry These Functional Groups Define Common Molecules Compounds And Reactions Biochemistry Functional Group Peptide Bond

0 Comments